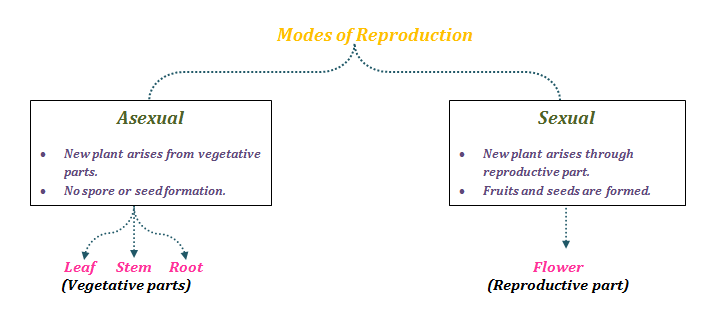
Describe the different methods of asexual reproduction Give examples SOLUTION Various methods of asexual reproduction are as follows (i) Vegetative propagation In this method, new plants are produced from vegetative parts of the plant such as roots, stems, leaves, buds etc It can be divided into two types (A) Natural vegetative propagation This type of vegetativeSexual, where plants are grown from seeds formed as a result of sexual reproduction inside the flower The plants that grow from seed may not be exactly identical to the parent plant asexual, where part of the parent plant is taken to make a new plant exactly the same Stem cuttings are an example of asexual propagationCan dormant seeds be stored longer than nondormant ones?

What Are The Different Ways Of Reproduction In Plants Give Examples Different How Or Rmjnaiion Take Place T Stud Evs Our Resources Meritnation Com
Seeds that will reproduce
Seeds that will reproduce- In plants, asexual reproduction is called vegetative propagation Vegetative propagation, like many things, has its advantages and disadvantages It is beneficial for plants that are well suitedEver wondered how seeds from one Plant get sown in a different area altogether?



Asexual And Sexual Reproduction In Plants Jennifer C
There are as many examples of sexual reproduction as there are animal species Mammals such as dogs, chimpanzees, whales or humans have sexual reproduction with internal fertilization and oogamy, they are also viviparous animals, so embryonic development will take place in the womb Birds, although they lay eggs as they are oviparous animals, also follow this sexual Seed production diagramAmong seed enterprises in the seed sector, for a more efficient delivery of a wider range of improved crop varieties and planting materials The final goal is to eventually develop a seed system which will be self sustaining, profitable and capable of delivering the Seed is the reproductive structure characteristic of all phanerogams The structure of seeds SEEDS They are plants that are not fully formed 5 PARTS OF A SEED A seed has 3 parts 1) Seed coat A cover that protects the seed 2) Embryo The baby plant 3) Stored food Seed coat Stored food Embryo 6 WE CAN CLASSIFY THE SEEDS ACCORDING TO Seed structure Water melons have flat small seeds Mangos and peaches have one seed
Plant reproduction is the production of new offspring in plants, which can be accomplished by sexual or asexual reproduction Sexual reproduction produces offspring by the fusion of gametes, resulting in offspring genetically different from the parent or parentsAsexual reproduction produces new individuals without the fusion of gametes, genetically identical to the parent plants40 Sexual Reproduction in Plants Mr C Biology 6 Wind Pollination Animal Pollination Petals Green or absent Brightly coloured, scented with nectar Pollen Large amounts, light and small Small amounts, sticky and spiny Anthers Large, loosely attached Small, firmly attached Stigmas Large and feathery, outside petals Small and Sticky, inside petalsEnglish examples for "reproduce by seed" It can reproduce by seed and it can form large colonies by spreading via its rhizomes Grazing by cattle reduces the plant's ability to reproduce by seed, so cloning is often more common The plant reproduces by seed and may spread vegetatively by sending out stolons The plant reproduces by seed and by sprouting from its root crown
Q2 Describe the different methods of asexual reproduction Give examples Answer The various modes of asexual reproduction in plants are as follows (i) Vegetative propagation It is the ability of a plant to produce new plants from roots, stems, leaves, and buds Vegetative propagation is divided into two types • Natural vegetative propagation This type of vegetative propagationThe phenomenon of Seed Dispersal helps in reproduction in plants But what exPlant reproductive system plant reproductive system Seed plants In the two great groups of seed plants, gymnosperms and angiosperms, the sporophyte is the dominant phase in the life cycle, as it is also in the vascular cryptogams;




Botanical Record Breakers Part 2 Of 2
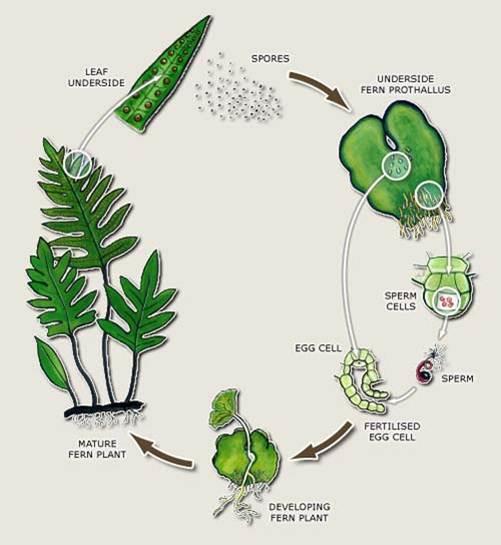



How Do Seed Plants Differ From Seedless Plants Socratic
Sexual Reproduction in Plants Reproduction in plants takes place sexually and asexually as well But the majority of the flowering plants reproduce sexually The flower is the reproductive part of a plant ie, both male and female gametes are produced by flowers Sexual reproduction in plants takes place in flowers The complete flowerVegetative reproduction is especially common in aquatic vascular plants (for example, surfgrass and eelgrass), from which fragments can break off, disperse in the current, and develop into new whole plants A minority of flowering plants can produce seeds without the fusion of egg and sperm (known as parthenocarpy or agamospermy)The multicellular seeds are a result of sexual reproduction, while spores are unicellular and a method of asexual reproduction Seeds are hardier and carry more nutrients for the developing embryo, while spores, being smaller, carry less food Seeds can be dispersed in various ways, like by animals, water, and wind, and germinate wherever they contact soil Spores can only be




What Are The Seed Pods On My Pink Oleander Oleander Plants Seed Pods Wonderful Flowers
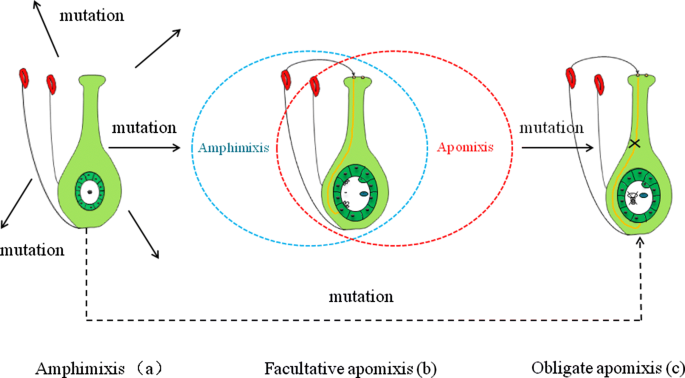



The Steps From Sexual Reproduction To Apomixis Springerlink
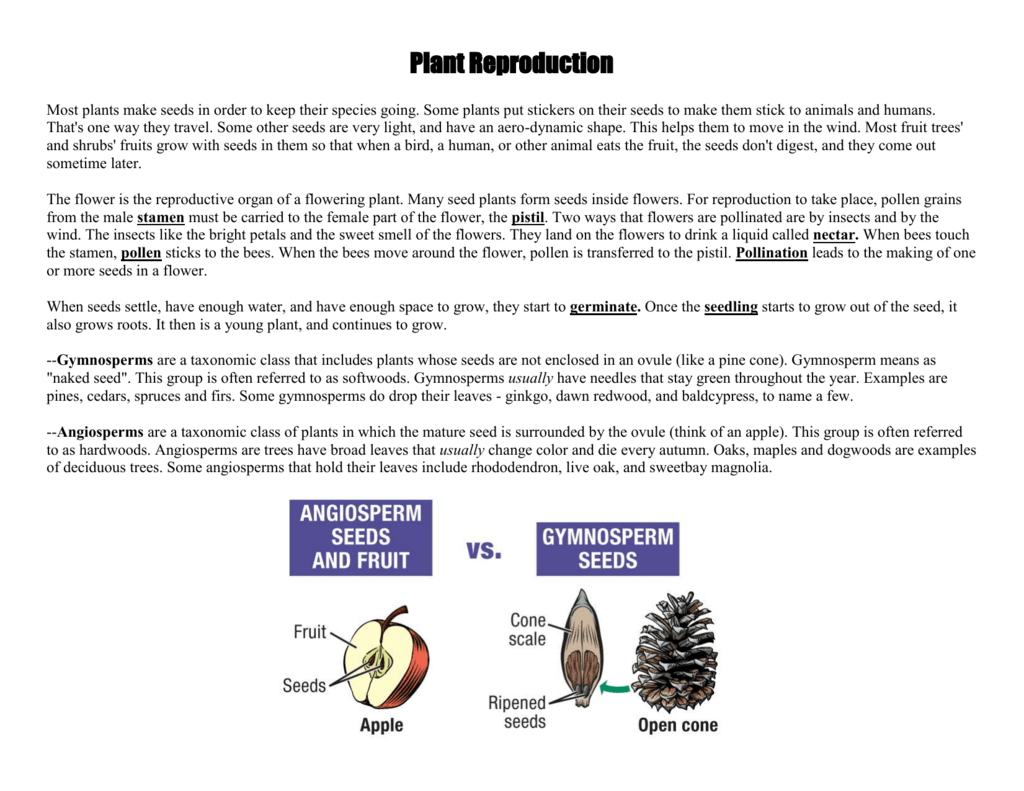
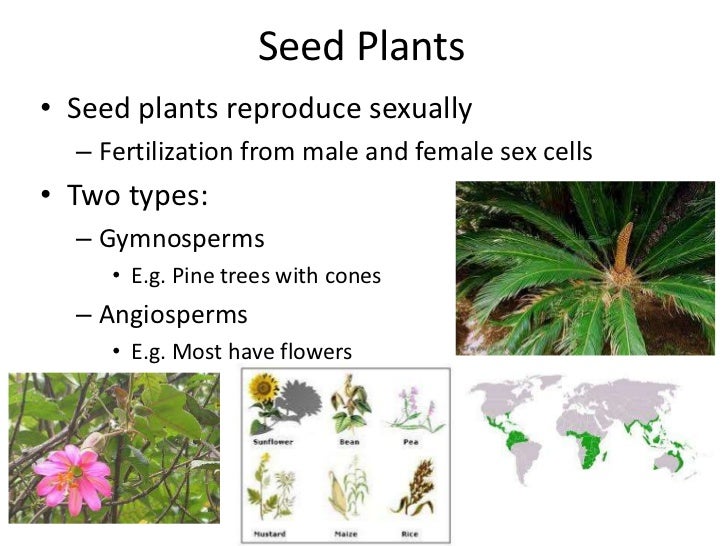
Gymnosperms are any type of vascular plant that reproduce via an exposed seed While most flowering plants, known as angiosperms, have a seed enclosed in an ovary or fruit, gymnosperms (which means "naked seeds") do not have covers on their seeds Some examples of nonflowering plants that are classified as gymnosperms includePlant reproduction without seeds Not every plant grows from a seed Some plants, like ferns and mosses, grow from spores Other plants use asexual vegetative reproduction and grow new plants from rhizomes or tubers We can also use techniquesGarden ☆ Seeds & Reproduction Collection by Jenaria's Realm 125 Pins • 263 Followers The Birds & the Bees of Growing!




Plants Without Seeds Plant Reproduction Dk Find Out
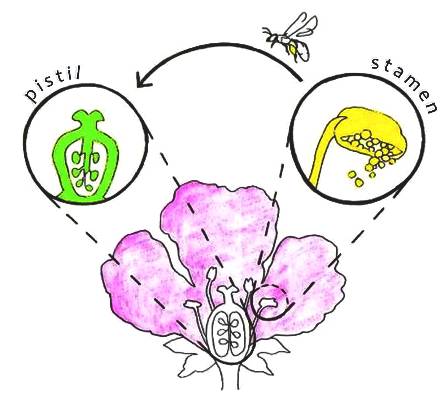



Flower Anatomy
An example of this is plants which belong to the Pea Family They produce seed pods which dry in the sun and suddenly split into two halves and disperse their seed Reproduction without seeds Reproduction is the production of new individuals or offspring in plants The relationship between pollinator and flower characteristics is one of the great examples of coevolution Following fertilization of the egg, the ovule grows into a seed The surrounding tissues of the ovary thicken, developing into a fruit that will protect the seed and often ensure its dispersal over a wide geographic range Not all fruits develop completely from anBut Sometimes no, for a seedlot that contains rotting pieces of fruit will probably go mouldy and the seeds die (See B 30–34 for more information on seed handling)
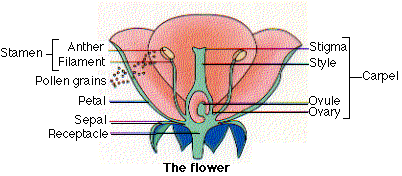



Sexual Reproduction In Angiosperms




Plant Propagation Wikipedia
Reproduction is the biological process where a new individual organism is produced by their parents In general, plants reproduce either asexually ie without seed formation or sexually ie with seed formationAlthough reproduction without sex is common in plants and for some species it represents their sole means of reproduction, most plants rely on sexual reproduction,Based on the distribution of seed plants above classification, it can be seen several examples of seed plants that we encountered in the environment around us, including the following Gymnosperm (gymnosperms), among others melinjo, pine, cycads Closed seed plants (Angiospermae) into pieces one such as corn, rice, coconut, and others Some seeds are dispersed by animals, especially spiny seeds with hooks which get attached to the bodies of animals and are carried to distant places Examples are Xanthium and Urena Some seeds are dispersed when the fruits burst with sudden jerks The seeds are scattered far from the parent plant




Plant Reproduction Let S Talk Science




Asexual Reproduction In Plants Biology For Majors Ii
Apomixis is a form of asexual reproduction in some species of grasses The parent plant produces seeds without fertilization Fragmentation is another form of asexual reproduction It involves new plants growing from small parts of the parent plant that fall to the ground For example, animals or the wind can break stems or leaves off plants The full responsibility for the reproduction of the plant is passed to the seeds produced by the plant before the end of the season In favorable climatic conditions, an annual plant can produce large amounts of seeds and can multiply so abundant that it can give the impression that it is perennial There are many plants that fall into thisVegetable Garden Garden Plants Backyard Plants Water Plants Herb Garden Container Gardening Gardening Tips Organic Gardening Plant Containers The Small Object Notes thesmallobject




What Are The Different Ways Of Reproduction In Plants Give Examples Different How Or Rmjnaiion Take Place T Stud Evs Our Resources Meritnation Com



Asexual And Sexual Reproduction In Plants Jennifer C
The example on the right whose seeds are dispersed by wind Sycamore Strawberry sexual reproduction of plants Name part B of the stamen and give its role in the sexual reproduction of plants Give a way in which the pollen from the flower of one plant can be transferred to the flower of another plant Name the cell that is formed when a male gamete (sperm) and a female gameteExamples of seed dispersal by wind;Seeds which have wings and hairy parachutes on them are carried by the wind Eg – sycamore, ash, maple, lime, dandelion and thistle When pods dry, they split open suddenly and shooting the seeds away from the parent plant and this is



Reproduction Different Modes Of Plant Reproduction Byju S




Reproductive Plant Parts Osu Extension Service
Plant reproductive morphology is the study of the physical form and structure (the morphology) of those parts of plants directly or indirectly concerned with sexual reproduction Among all living organisms, flowers, which are the reproductive structures of angiosperms, are the most varied physically and show a correspondingly great diversity in methods of reproductionThe gametophytes are microscopic parasites on the sporophytes In the gymnosperms, the seeds occur individually, exposed at the ends of stalks,I can give examples of the type of reproduction carried out by named organisms ?




What Are Some Forms Of Plant Propagation



Basic Plant Life Cycle And The Life Cycle Of A Flowering Plant Gardening Know How
7 I can explain the relationship between the number of sex cells produced and theReproduction ma lie asexual •tr sexual Different organisms have different reproductive strategies For example Some species of oak does not reproduce until it becomes year old Then it produces large number of seeds each year Annual desert wildflowers produce many small seeds and then die The reproductive strategies depend on three factors Clutch size;5 I can define fertilisation as the fusion of the nuclei from the male and female sex cells ?




Science Plant Reproduction Without Seed English Youtube



Saving Seed Will The Seed Produce Plants Similar To The Plant It Was Collected From
Angiosperm reproduction The process of reproduction of angiosperm plants begins with pollination Pollination happens when pollen is moved from the anther (a male organ of the flower) to the stigma (a female organ of the flower) The stigma can be on either the same or a different flower that the pollen came from As shown below, when a pollen grain reaches the stigma, itUrena and Xanthium are examples of this These seeds get dispersed because of sudden jerks in animal movement Castor and Balsam are examples of this This situation is seed dispersal And in case of fruit formation, once it ripens, the other parts of the flower fall off Some examples of sexual reproductive plants are mango, apple, almond, andGive two examples All plants can reproduce through seeds, except for those hybrids/cultivars that are so radically modified that they have lost reproductive function Seedless watermelon and hybrid tea roses would be examples of those that CANNOT reproduce form seed 490 views




Angiosperm Definition And Examples Biology Online Dictionary




Seed Form Function Dispersal Germination Britannica
Seeds dispersed by the wind are easier to investigate than seeds dispersed by other methods For example, you could release sycamore seeds and measureThe lush palms on tropical shorelines do not depend upon water for the dispersal of their pollen, fertilization, or the survival of the zygote, unlike mosses, liverworts, and ferns of the terrain Seed plants, such as palms, have broken free from the need to rely on water for their reproductive needsSeed dispersal is an important aspect of plant reproduction If not suitably dispersed, seeds will germinate very close to their parent plant This means that the seedlings must compete with one another and, of course, the parent plant for space, light, water and nutrients Studying wind dispersal can bring together important scientific ideas in biology and physics These include




4 02 Methods Of Plant Propagation Sexually And Asexually Propagating Plants Ppt Download




Plant Sexual Reproduction Educational Video For Kids Youtube
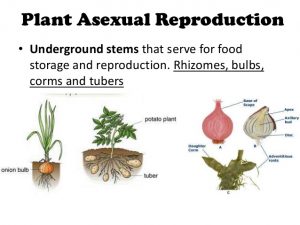
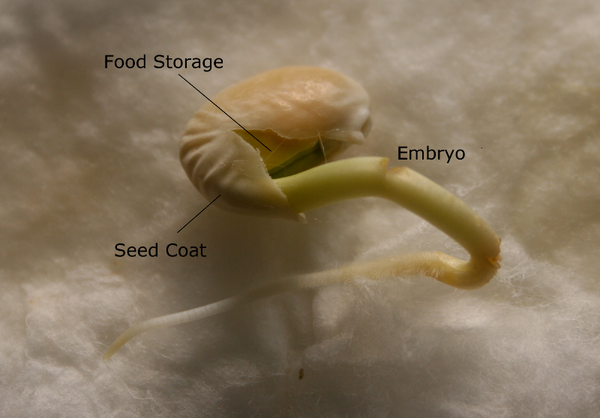
Vegetative reproduction results in new plant individuals without the production of seeds or spores Many different types of roots exhibit vegetative reproduction The corm is used by gladiolus and garlic Bulbs, such as a scaly bulb in lilies and a tunicate bulb in daffodils, are other common examples of this type of reproduction A potato is a stem tuber, while parsnip propagates fromExamples of seed production in a sentence, how to use it 21 examples Mechanized dry seed production in pigeonpea Mechanized dry seed production Seed Formation If all the endosperm is not absorbed by the developing embryo the seed is an endospermic seed eg Maize 44 Seed types and structure Seed embryo Plumule (immature shoot) Radicle (immature root) Cotyledon (food supply or seed leaf) endosperm Food store All seeds In some seeds 45



Reproduction In Plants Psle Science



1
Sometimes yes for example a seedlot with hard seed coats will usually keep best if they have not yet been pretreated;It is possible for plants to reproduce asexually (ie without fertilisation in flowers) Three methods of plant asexual reproduction are Bulbs underground food storage organs with fleshy leavesSeed size and predation Seeds form the main source of food for many birds, rodents, ants, and beetles Harvester ants of the genus Veromessor, for example, exact a toll of about 15,000,000 seeds per acre (37,050,000 seeds per hectare) per year from the Sonoran Desert of the southwestern United States In view of the enormous size range of the predators, which include



Plant Reproduction



How Do Trees Reproduce Quora
Vegetative reproduction is extremely common in perennial plants, especially in grasses and aquatic plants, and it can have dramatic consequences The waterweed Elodea canadensis, for example, was introduced into Britain in about 1840 and spread throughout Europe by 10 entirely by vegetative reproduction (6) This is an example of sexual reproduction However, this is not the only way to propagate a plant Other ways do not involve seeds and utilize asexual reproduction instead When plants reproduce6 I can explain the difference between internal and external fertilisation and state the advantages and disadvantages of each ?




Plant Reproduction Wikipedia
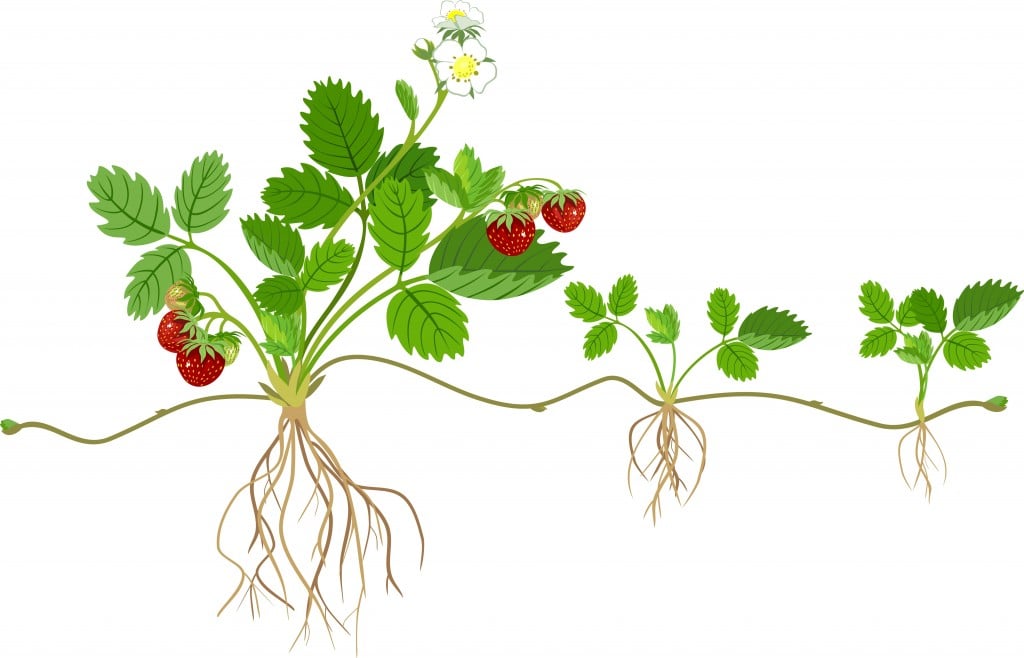




Plant Reproduction How Do Plants Reproduce



1




Plant Fertilization Process Definition Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
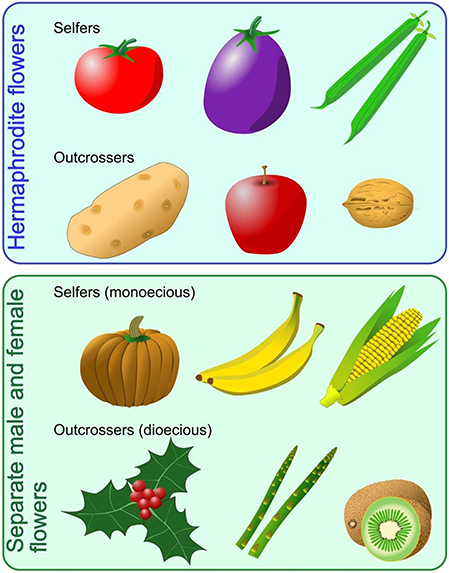



Flower Power A Close Look At Plant Reproduction Frontiers For Young Minds



Advantages And Disadvantages Of Asexual Reproduction In Plants Science Online



Plant Reproductive Development And Structure Boundless Biology



Plant Reproduction Seed Plants




Biology Reproduction Notes




There S More Than One Way To Make A New Plant Discovery Express




Plant Reproduction Without Seeds Science Learning Hub




Plant Reproduction Science Learning Hub




Loh Pei Hang D 2 3 Plants Reproduce



Sexual Reproduction In Plants Learn Biology Class 7 Amrita Vidyalayam Elearning Network
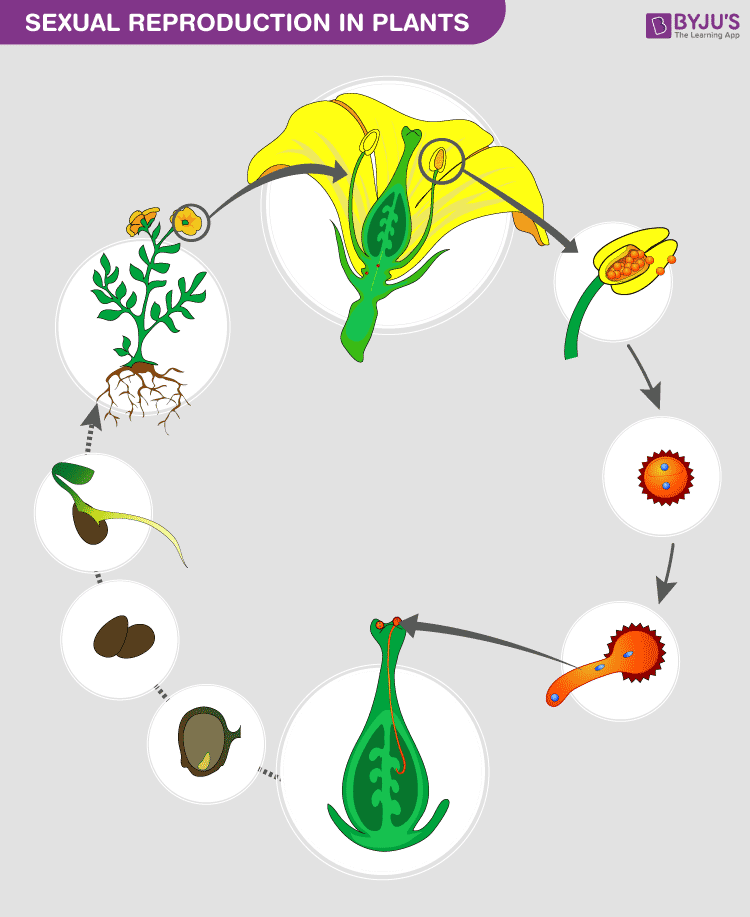



Sexual Reproduction In Plants Features And Its Process
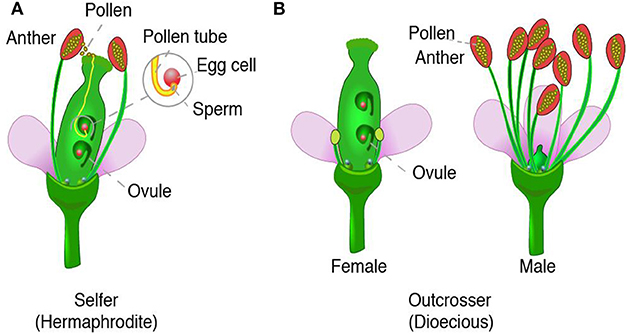



Flower Power A Close Look At Plant Reproduction Frontiers For Young Minds




Seed Form Function Dispersal Germination Britannica



Propagation




Plant Propagation Sexual Reproduction Of Plants Ppt Download




13 Propagation Nc State Extension Publications
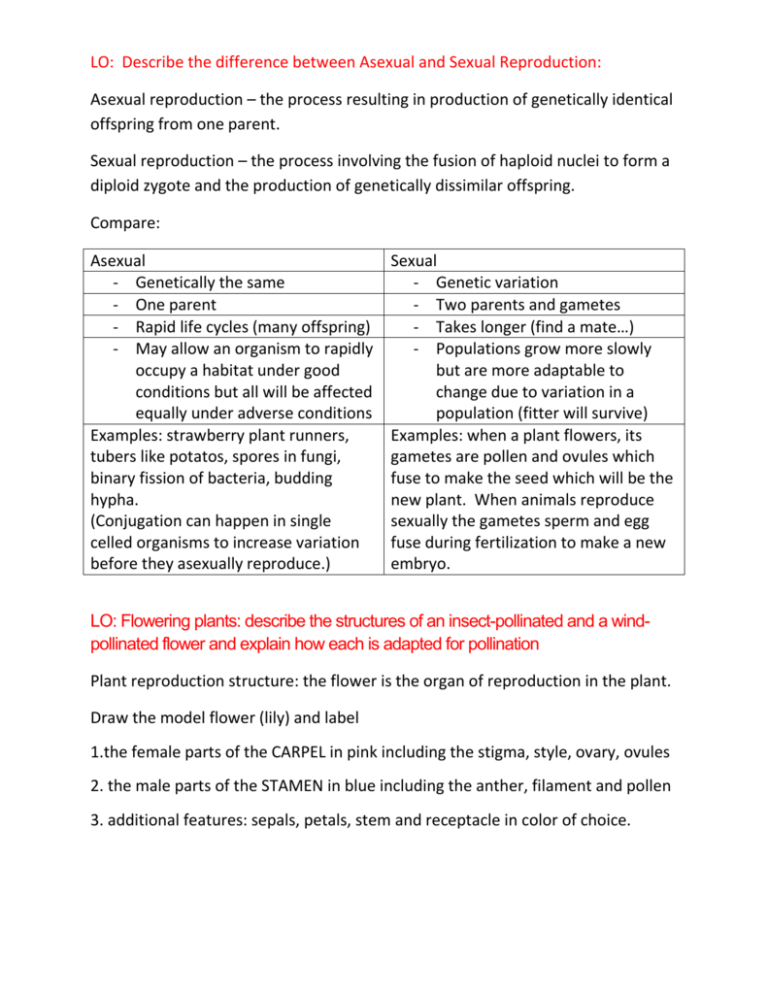



Lo Describe The Difference Between Asexual And Sexual




The Seed Structure Functions Dispersion Concepts Videos Examples




Plant Reproduction Bioninja




Flowering Plants Life Cycle Examples Study Com




Many Seed Plants Can Reproduce Sexually Or Asexually Chegg Com




13 Propagation Nc State Extension Publications




Fruits Flowers And Seeds Biology Online Tutorial




Plant Propagation Sexual Reproduction Of Plants Ppt Download




Seed Dispersal Reproduction In Plants Don T Memorise Youtube




Flowering Plant Reproduction Development And Chegg Com




Vegetative Propagation In Plants Definition Methods Examples Video Lesson Transcript Study Com



Asexual And Sexual Reproduction In Plants Jennifer C




Pin On Xaiden
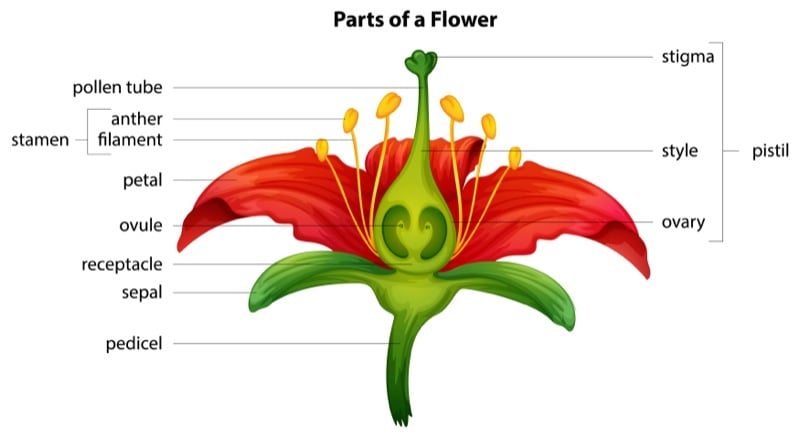



Plant Reproduction How Do Plants Reproduce




Plant Reproduction Bioninja




Angiosperms Features Classification Reproduction Videos Examples



Asexual And Sexual Reproduction In Plants Jennifer C




Examples Of Possible Log Log Relationships Between Direct And Accessory Download Scientific Diagram
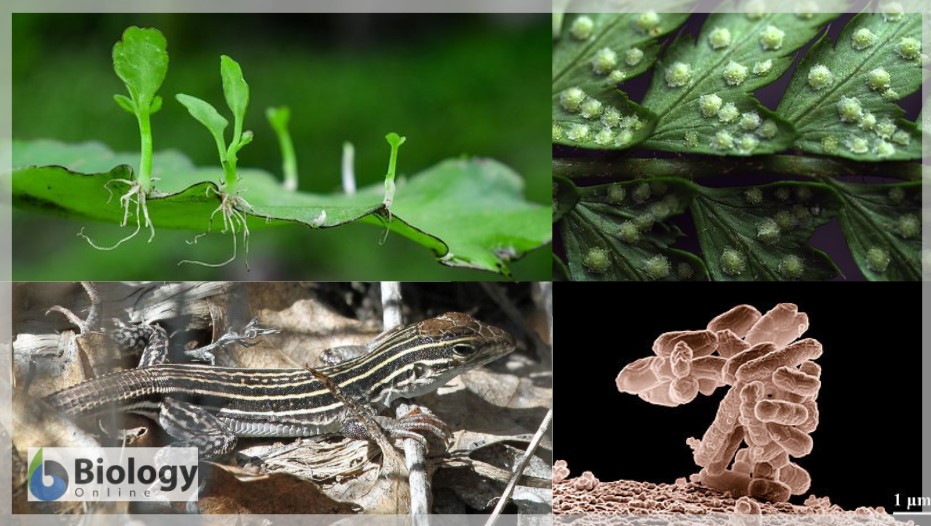




Asexual Reproduction Definition And Examples Biology Online Dictionary
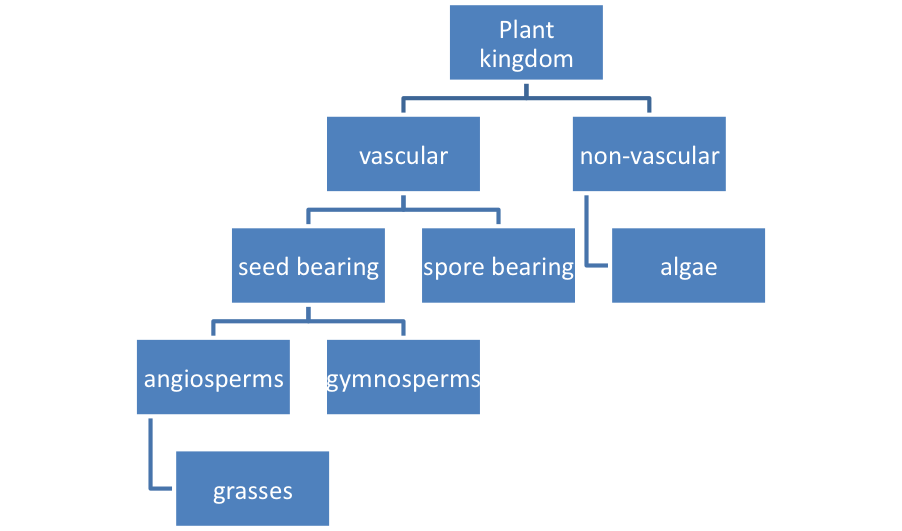



Lesson 4 Plant Classification Mpalalive




Plant Reproduction Seed Plants




Seed Wikipedia




Chapter 22 Mcgraw Hill Higher Education



Introduction To Reproduction Plants Animals Types Videos Examples
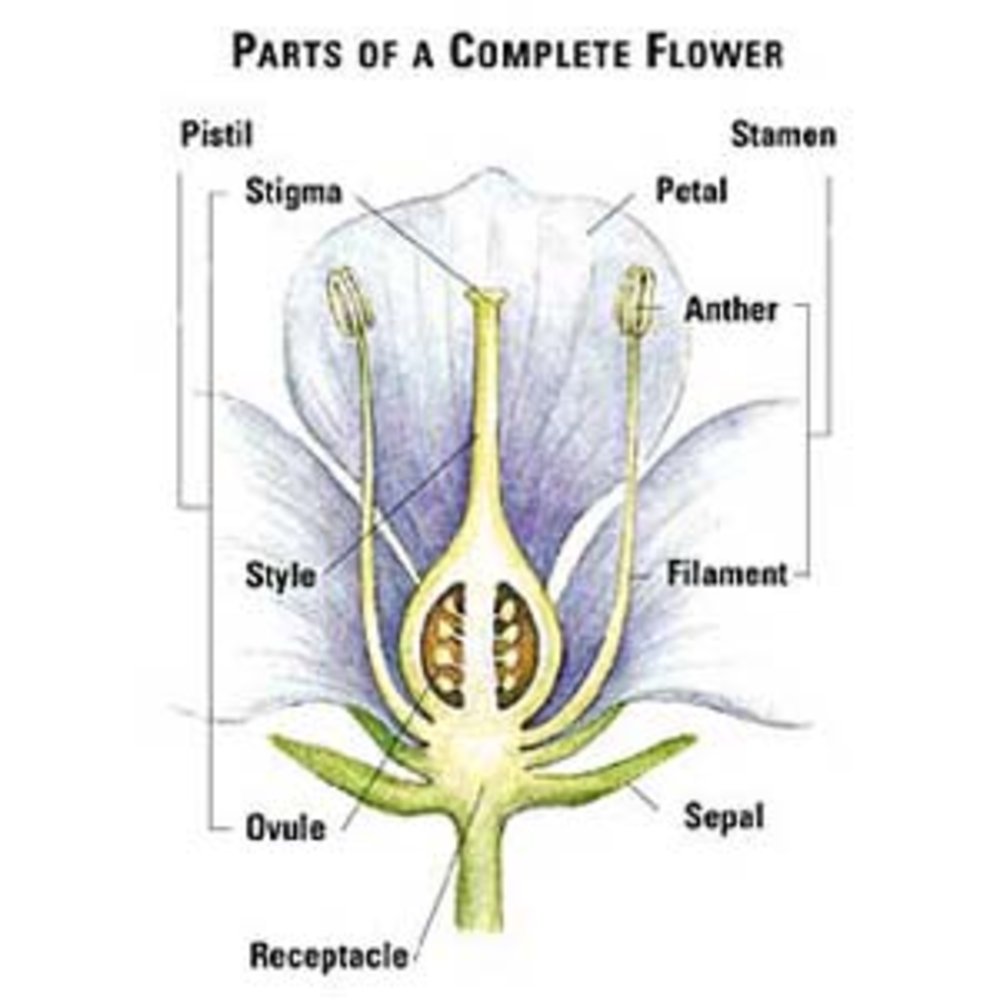



Flowers Sunset Magazine
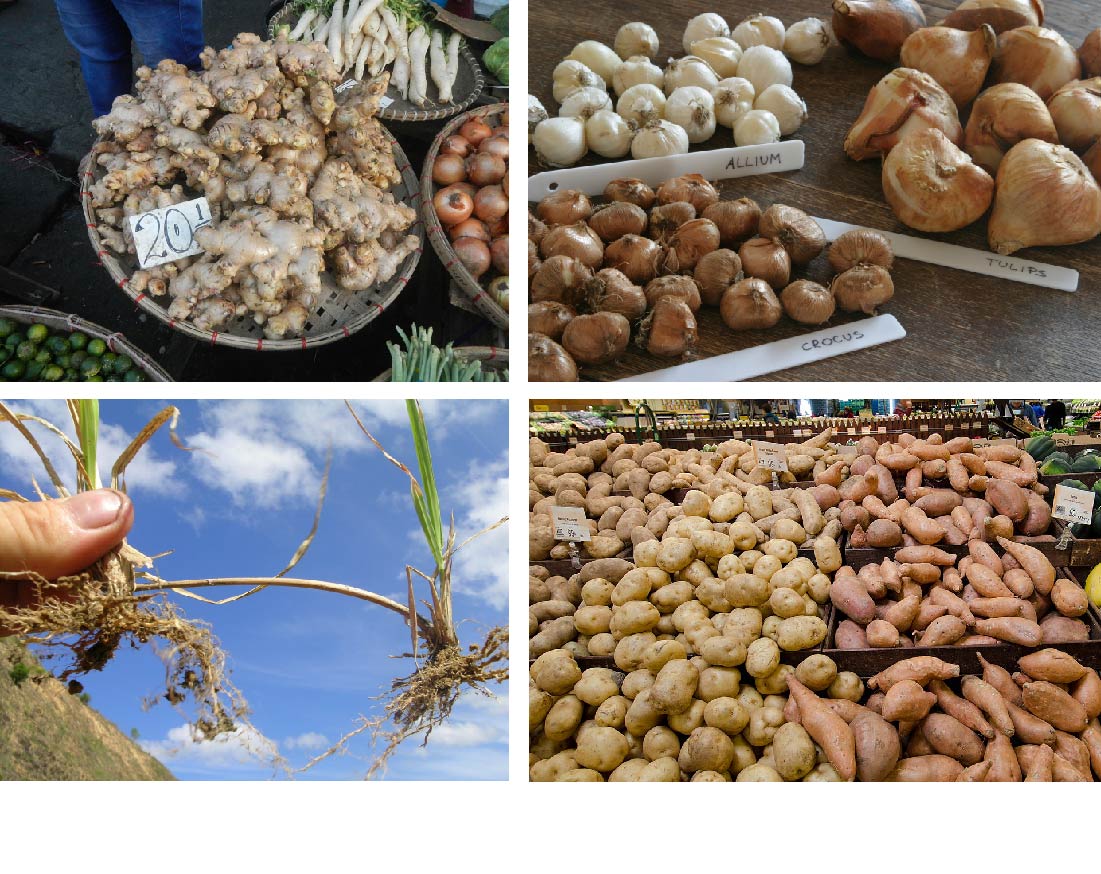




Plant Reproduction Let S Talk Science




Seed Form Function Dispersal Germination Britannica
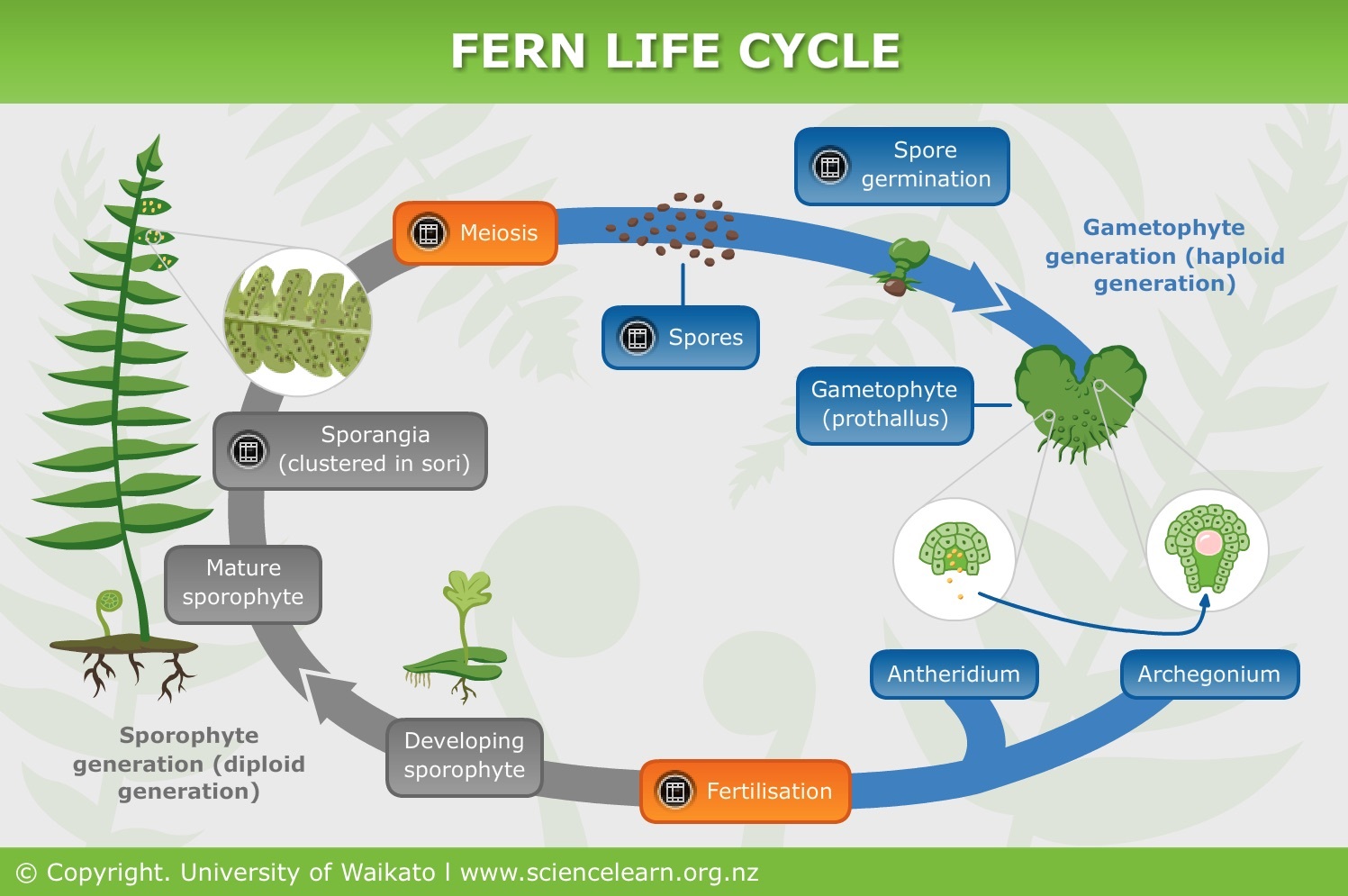



Plant Reproduction Without Seeds Science Learning Hub



Asexual And Sexual Reproduction In Plants Jennifer C
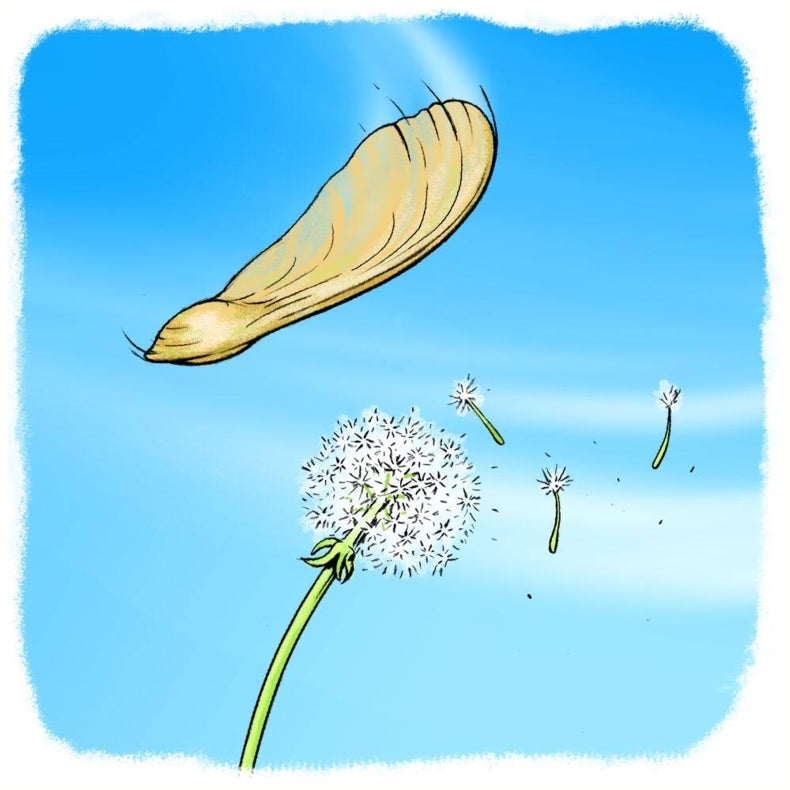




Gone With The Wind Plant Seed Dispersal Scientific American
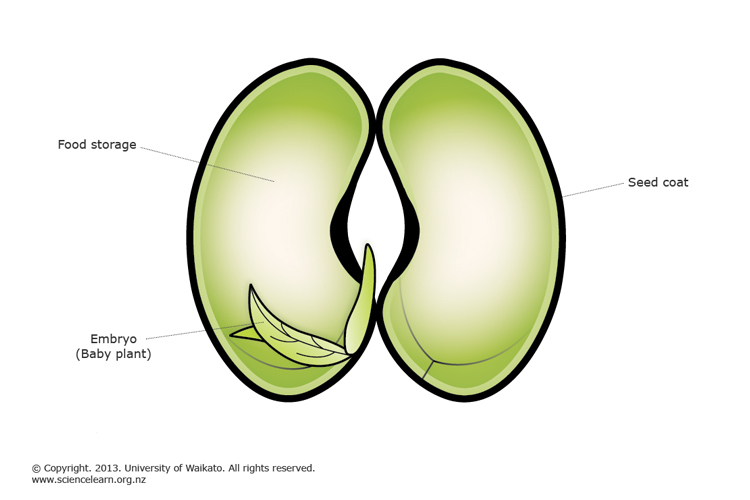



Plant Reproduction Science Learning Hub




Flower Dissection Activity Review There Are Two Types Of Plants Plants With Seeds And Plants Without Seeds Ppt Download
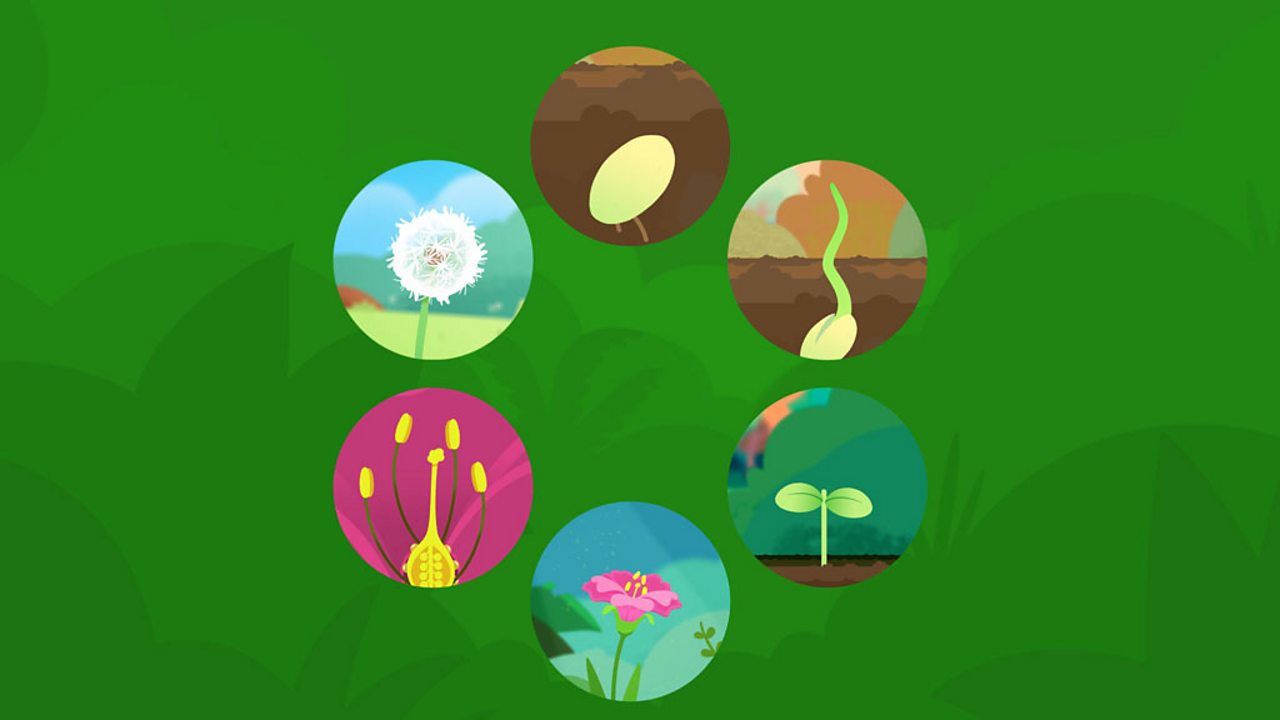




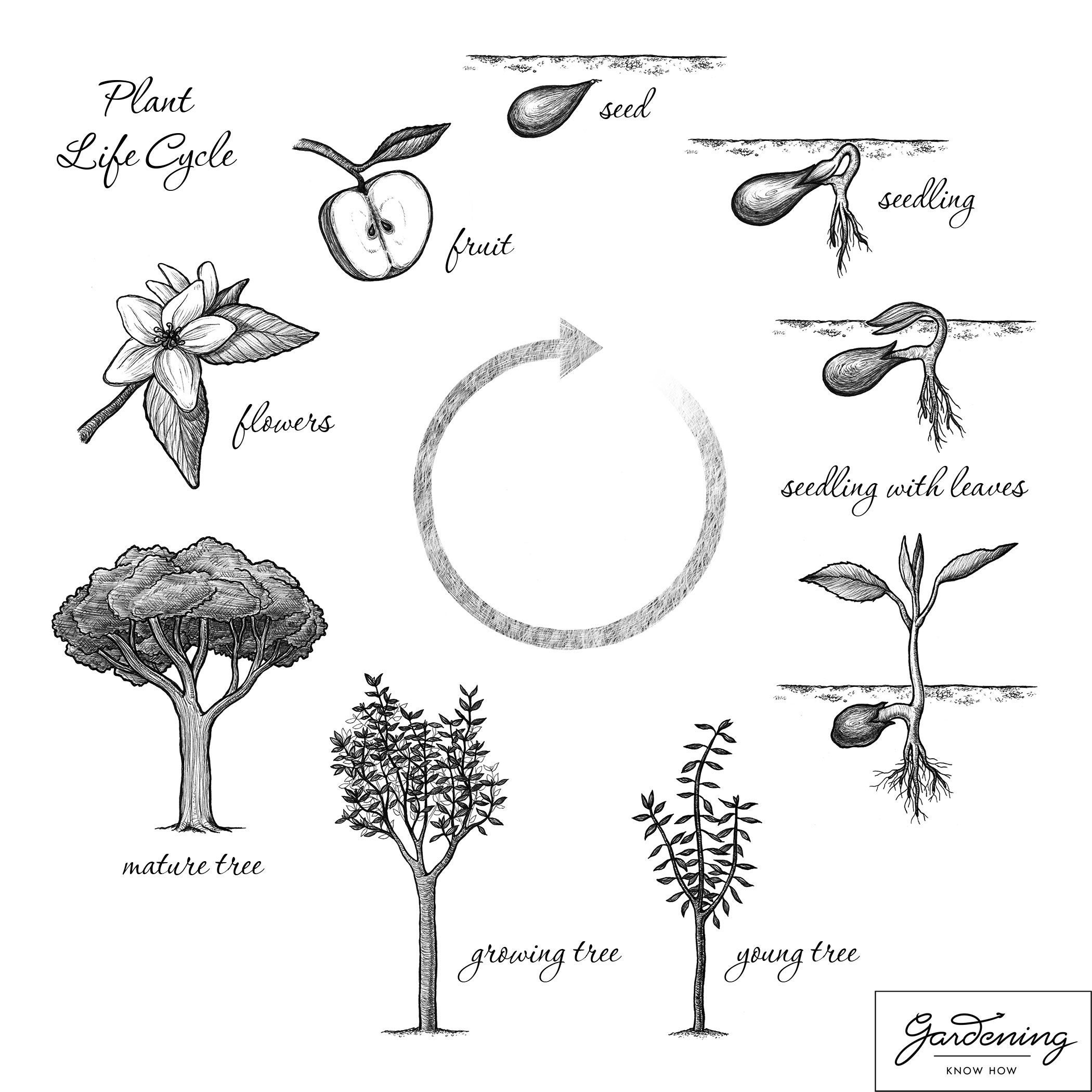
What Are The Stages Of A Plant S Life Cycle c Bitesize



Ginseng Reproduction




Definition Of The Seed Advantages And Disadvantages Of Seed Propagation




What Is A Seed Lesson For Kids Video Lesson Transcript Study Com



Reproduction In Plants Biology Encyclopedia Cells Body Examples Function Process Animal Different Organisms Chromosomes Organs




Ovary Botany Definition Structure Britannica




There S More Than One Way To Make A New Plant Discovery Express



Asexual Reproduction Biology Ii



Reproduction In Plants Biology Encyclopedia Cells Body Examples Function Process Animal Different Organisms Chromosomes Organs




Chapter 12 Plant Propagation




Pollination And Seed Dispersal Science Video For Kids Grades K 2




Plants That Reproduce Sexually World Today News
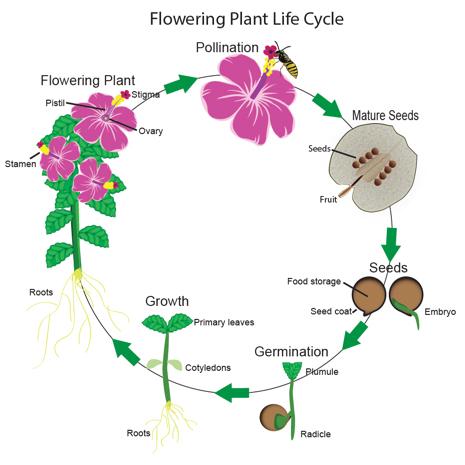



Flowering Plants Life Cycle Lovetoknow




Types Of Reproduction In Plants Youtube



Sexual And Asexual Reproduction In Plants




Biology Reproduction Notes



Reproduction In Plants Biology Encyclopedia Cells Body Examples Function Process Animal Different Organisms Chromosomes Organs




Reproductive Systems And Evolution In Vascular Plants Pnas



3



Q Tbn And9gcqy9wuzklahycc9 Ktqoconahtwyb6c2a37il9scvsrouasu38t Usqp Cau




Gymnosperms Naked Seed Plants An Overview Of Biodiversity




Reproduction In Human And Plants Male Reproductive System
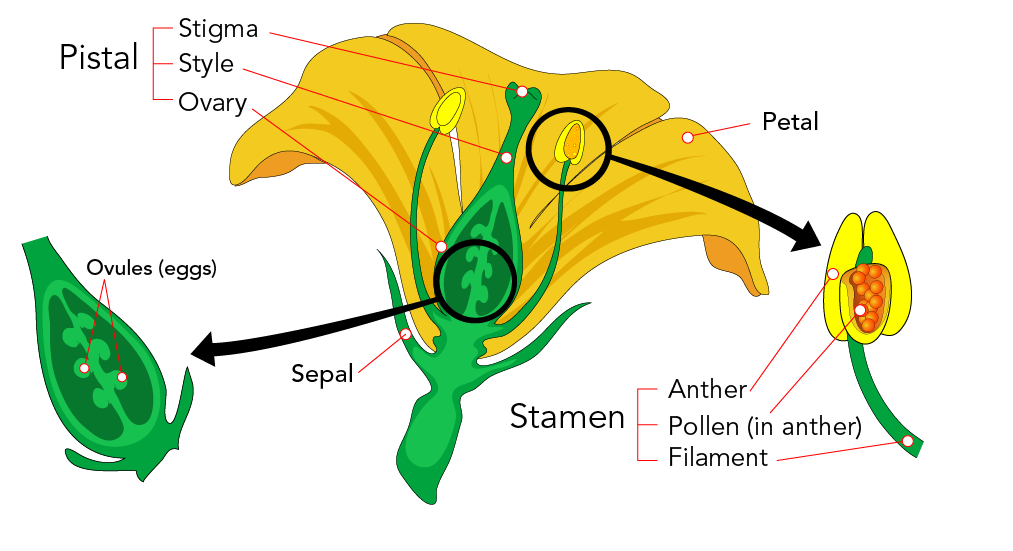



Plant Reproduction Let S Talk Science




Loh Pei Hang D 2 3 Plants Reproduce
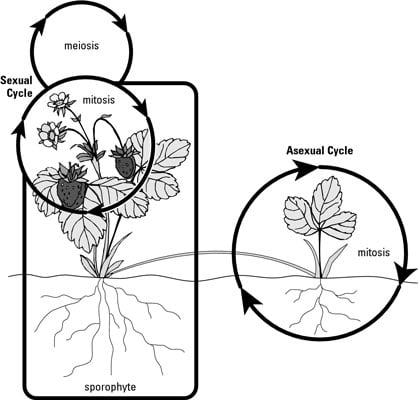



Plant Reproduction Dummies




Reproduction Different Modes Of Plant Reproduction Byju S



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿